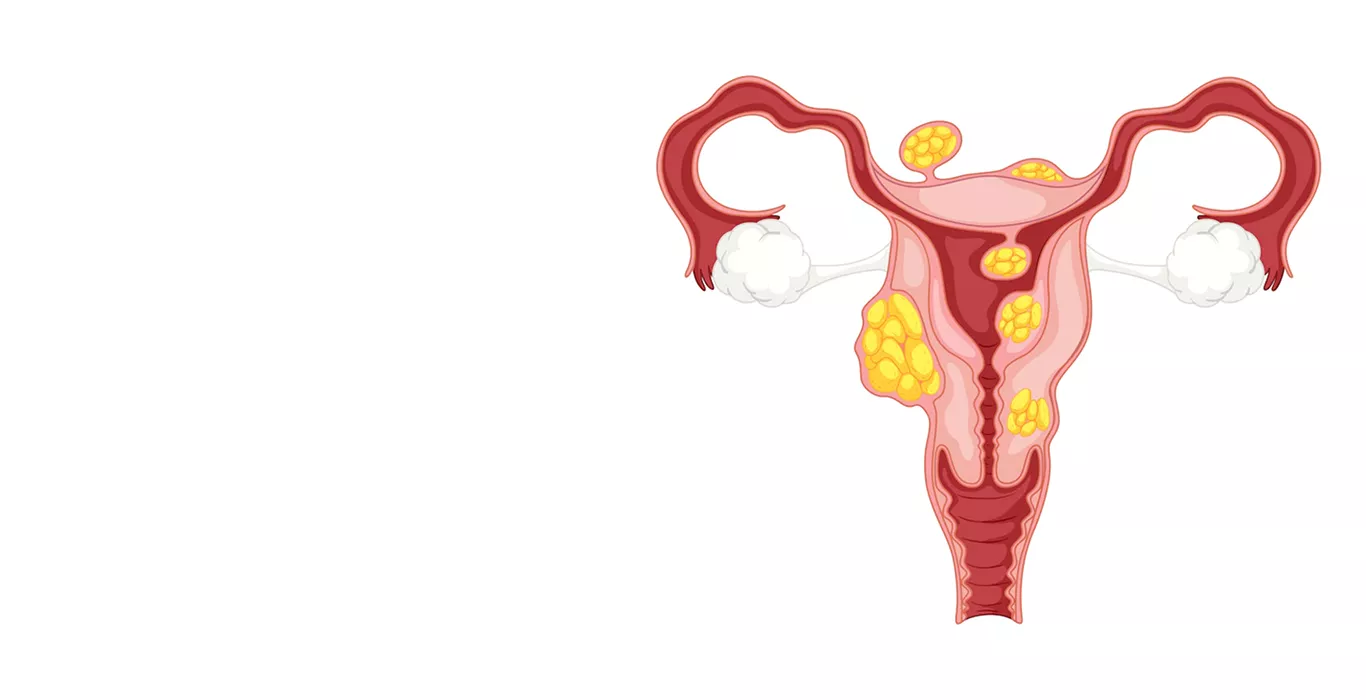
What are Uterine Fibroids?
Uterine fibroids are noncancerous growths that develop in or on a woman's uterus. These fibroids that are also known as leiomyomas or myomas, often develop during a woman’s reproductive years. Uterine fibroids usually vary in size and location. These growths are made up of muscle and fibrous tissue and can range from small, seed-like nodules to bulky masses that can distort the uterus. They aren't associated with an increased risk of uterine cancer and are quite common, with many women experiencing them at some point in their lives.
Uterine fibroids are non-cancerous muscular tumours that grow inside the uterus, on its outer surface, or within the uterine wall. These growths are common among women of reproductive age and may influence menstrual patterns, pelvic comfort, and, in some cases, fertility. Their size may vary from tiny nodules to large masses that alter the shape of the uterus.
What are Uterine Fibroids?
Uterine fibroids or leiomyomas (fibroids) are abnormal growths composed of muscle and tissue that develop in or on the wall of your uterus. These growths are commonly benign (noncancerous) and are the most common noncancerous tumours in females. Their size can range from minute nodules to huge masses that can change the shape of the uterus. Uterine fibroids may cause a wide range of symptoms, including pain and heavy, irregular vaginal bleeding. On the contrary, a person can also be symptom-free and not know they have fibroids. Treatment of fibroids usually depends on your symptoms.
What are the Types of Uterine Fibroids?
Uterine fibroids are classified differently based on their location and how they are attached. Some common types of uterine fibroids are:
- Intramural fibroids : These fibroids are located within the muscle layer of the uterine wall. They are the most commonly occurring type of uterine fibroids.
- Submucosal fibroids : These fibroids develop beneath the inner lining of the uterus.
- Subserosal fibroids : This kind of fibroid grows under the lining of the outer surface of the uterus. They can get really big and extend to the pelvis.
- Pedunculated fibroids : Being the least typical, these fibroids are connected to the uterus by a stalk or stem. Generally, they often appear mushroom-shaped because they have a stalk and then a wider top.
What are the Causes of Uterine Fibroids?
There is no known cause of fibroid development, though several factors may contribute. Causes of uterine fibroids include:
- Hormones : Estrogen and progesterone cause the uterine lining to thicken each month during menstruation. They appear to influence fibroid growth as well. Fibroids tend to shrink when hormone production is slow during menopause.
- Family History : The condition of the uterine fibroids might be hereditary. In case your family members, such as your grandmother, sister or mother, had a fibroid history, then you may be at an increased risk of getting it in the future.
- Pregnancy : Pregnancy causes the level of estrogen and progesterone hormones in the body of a woman to increase, and due to the same, fibroids can grow and develop at a fast rate during the period of pregnancy.
These are some of the major causes of uterine fibroids.
What are the Symptoms of Uterine Fibroids?
Some women may not show any signs and symptoms of uterine fibroids, especially when the fibroids are small in size, non-cancerous, and do not require any treatment. They do not come across any symptoms of uterine fibroids until they become significant in size. Large fibroids can cause some symptoms. Common symptoms of uterine fibroids are:
- Heavy or prolonged menstrual bleeding : This is a symptom which is most common with submucosal fibroids, which grow on the interior of the uterus, and the intramural fibroids, which grow embedded in the muscular uterine wall. The symptom can significantly change a person's life.
- Pelvic pressure or discomfort : Pain in the lower abdomen is another symptom of fibroids. Large fibroids may cause pain in women's abdomen which is constant.
- Frequent urination : Fibroids can develop in the area of the uterus that is close to the bladder and intestines. If fibroids become large enough, they can push against the bladder, causing the frequent need to urinate. In contrast, pressure on the bowel from fibroids can cause constipation.
- Lower back pain : Pelvic pain and low back pain are common early symptoms of uterine fibroids. The pain may be sharp or similar to your menstrual cramps but more intense.
- Anaemia due to heavy bleeding : Because of excessive blood loss during their menstrual periods, women may become anaemic and feel pain in their legs due to lack of strength.
How are Uterine Fibroids Diagnosed?
Diagnosis is also important in determining the size, number and location of the fibroids, as these can all affect fertility as well as what treatment options are viable. Doctors use the following to obtain the exact size of fibroids:
1. Ultrasound (Primary Diagnostic Tool)
- Transvaginal ultrasound: It provides a short and clear image of the uterus and fibroids.
- Abdominal ultrasound: It is helpful in the assessment of large fibroids or those that come out of the uterine wall.
Ultrasound is the most commonly used option since it is precise, available and non-invasive.
2. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
Detailed imaging provided by the MRI is often required for:
- Large or multiple fibroids
- Complicated cases where exact mapping is necessary
- Pre-surgical planning
MRI evaluates fibroid composition, vascularity, and proximity to adjacent structures.
3. Hysteroscopy
Used especially for submucosal fibroids:
- A narrow tube is passed through the cervix to examine the inside of the uterus.
- It evaluates for distortion of the cavity and allows removal of fibroids at the same time.
4. Sonohysterography (Saline Infusion Sonography)
The method involves introducing saline into the uterus to improve picture clarity. Helpful in assessing the following:
- Location of submucosal fibroid
- Uterine cavity shape.
- Whether fibroids are affecting fertility
Importance of Early Detection
Early diagnosis allows:
- Enhanced preparation for pregnancy
- To avert complications including anaemia
- Management before fibroids grow larger
- Timely removal if they affect fertility
A full diagnostic workup allows for interventions that can be tailored to your reproductive goals.
How are Uterine Fibroids Treated?
Symptoms of most fibroids are non-existent and do not necessitate treatment. Actually, they usually diminish or fade away upon the occurrence of menopause. However, in case fibroids are producing some unpleasant symptoms, there are different medical interventions that may be used. Different treatments can be administered according to the symptoms, the intensity of the symptoms as well as the site of the fibroids which can be suggested by a doctor.
1. Medical Management
In order to manage uterine fibroids, the prescription of medication is done to control the level of hormone in order to reduce the size of the fibroids.
Releasing hormone (GnRH) agonists such as leuprolide (Lepron) aid in reducing the amount of estrogen and progesterone hormones. Drastic reductions in the concentrations of these hormones will consequently cease menses and fibroid will shrink. GnRH agonists such as cetrorelix acetate and ganilrelix acetate also aid in reducing fibroids. They assist in suppressing your body to secrete FSH (Follicle-stimulating hormone) and LH (Luteinizing hormone).
Other alternatives are also available that will assist in managing menstrual bleeding and pain, but will not reduce or decrease fibroids. These include:
- Birth Control Pills
- An intrauterine device (IUD) which releases the progestin hormone e.g. Mirena.
- Over the counter (OTC) anti-inflammatory pain relievers including ibuprofen etc.
2. Surgical procedures
- Myomectomy : This surgery is a removal of fibroids whereby the uterus remains intact hence it can be adopted by individuals who wish to retain their fertility.
- Hysterectomy : This is a medical procedure performed on the uterus to remove fibroids in the uterus permanently and permanently sterilize the person.
3. Non-surgical procedures
As well as traditional surgical techniques to treat fibroids, non-surgical treatments are also available.
4. Uterine artery embolisation (UAE)
Another method of treating fibroids, other than a hysterectomy or myomectomy, is uterine artery embolisation (UAE). It could be prescribed to women having large fibroids.
Tailored Treatment Approach
Every woman’s condition is unique. A personalised plan takes into consideration:
- Severity of symptoms
- Fibroid size and location
- Age and reproductive plans
- Previous treatments
- Overall health
Indira IVF emphasises fertility-friendly management, ensuring treatments align with the goal of achieving pregnancy whenever desired.
When Should You See a Doctor for Uterine Fibroids?
When fibroid symptoms start to disrupt normal living or the fertility ambitions, then medical assistance should be sought.
Key Indicators to Consult a Specialist:
- Heavy or prolonged menstrual bleeding
- Extreme pain or contractions in the pelvis.
- Difficulty conceiving
- Abdominal size swelling rapidly.
- Continuous tiredness because of anaemia.
Early evaluation prevents complications and supports better reproductive outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Can uterine fibroids lead to cancer?
Fibroids are nearly always benign. The possibility of them developing into cancer is extremely rare.
Can I still get pregnant if I have uterine fibroids?
Many women with fibroids conceive naturally. Nonetheless, implantation or pregnancy complications may be caused by the presence of fibroids distorting the uterine cavity. Therapy can enhance the ability to give birth.
Are there any lifestyle changes that can help manage uterine fibroids?
Healthy weight, low carbohydrate diet, stress management, and exercise can help in maintaining the balance of hormones and well-being.
Can uterine fibroids shrink on their own?
Some fibroids can be reduced by menopause, when the hormone levels decrease. This however differs with each person.
Is there a risk of uterine fibroids returning after treatment?
Fibroids may reoccur after myomectomy. It is dependent on age, fibroid count, and hormones.
What is the most accurate way to diagnose uterine fibroids?
The main form of diagnostic procedure is the transvaginal ultrasound, with MRI giving detailed mapping in the complex cases.
When should uterine fibroids be removed?
Removal is recommended in cases of fibroids that are characterised by severe symptoms, excessive bleeding, pressure, infertility or disturbance of the uterine cavity.
Is surgery always required for uterine fibroids?
No. Fibroids may be treated using medicines or with observation in case of mild symptoms.
Do uterine fibroids affect IVF treatment?
Fibroids that disfigure the uterine cavity can have implications on embryo implantation. Treatment of such fibroids will enhance the success rates of IVF.
What is the recovery time after fibroid removal surgery?
Recovery time varies:
- 1. Hysteroscopic myomectomy: 1-3 days.
- 2. Laparoscopic surgery: approximately 2 weeks.
- 3. Open surgery: several weeks
Can uterine fibroids grow during pregnancy?
Hormonal changes during pregnancy cause some fibroids to grow, although a lot of them are stable.
Who can get uterine fibroids?
Fibroids are common among women who are at the reproductive age; that is, between the ages of 30 and 50 years.
Do uterine fibroids affect fertility?
Some fibroids particularly submucosal ones can disrupt implantation, lead to miscarriage or influence the IVF results.
Pregnancy Calculator Tools for Confident and Stress-Free Pregnancy Planning
Get quick understanding of your fertility cycle and accordingly make a schedule to track it
Get a free consultation!