Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that develop on or within the ovaries, most often harmless and sometimes resolving on their own, especially during the menstrual cycle. While many cysts do not cause symptoms, some can lead to pain, irregular periods, or fertility issues.
Understanding ovarian cysts—including their causes, types, symptoms, and potential complications—helps women take control of their reproductive health. Diagnostic procedures can identify cysts early, and treatment options range from watchful waiting and hormone therapy to minimally invasive surgery and lifestyle management strategies.
What are Ovarian Cysts?
Understanding ovarian cysts is important: these fluid-filled sacs develop on the ovaries and are more common than most women think. While a majority of cysts are benign and may disappear without intervention, some can lead to discomfort, irregular periods, or even fertility challenges. Early detection is key to preventing complications and maintaining reproductive health.
At Indira IVF, we help women navigate these challenges with precise diagnosis and personalised treatment plans. Understanding the causes, types, and symptoms of ovarian cysts empowers you to protect your reproductive health with confidence.
What are The Types of Ovarian Cysts?
Ovarian cysts can be of the following categories:
- Functional cysts, including follicular and corpus luteum cysts, are hormone-related and generally develop during ovulation.
- Dermoid cysts, or mature cystic teratomas, can contain ectodermal tissue such as hair, skin, or teeth.
- Endometriomas are ovarian cysts resulting from endometrial tissue deposits linked to endometriosis.
- Cystadenomas originate from the ovarian surface epithelium and may be filled with serous or mucinous fluid.
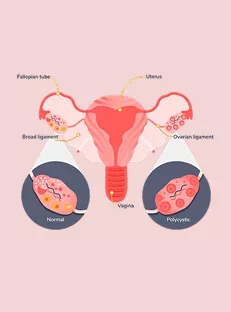
- Women with PCOS often have polycystic ovaries, where multiple small follicles remain unovulated.
What are The Causes of Ovarian Cysts?
Many women develop ovarian cysts due to causes such as:
- Hormonal imbalance
- Ovulation difficulties
- PCOS
- Endometriosis
- Natural changes during pregnancy
What are the Symptoms of Ovarian Cysts?
There are some common and severe symptoms of ovarian cysts, which are mentioned below
Common Symptoms
- Pelvic pain
- Bloating
- Irregular periods
- Pain during intercourse
- Frequent urination
Severe Symptoms (High-Alert)
- Sudden, intense pelvic pain (signs of ovarian cyst rupture)
- Severe abdominal pain with nausea or vomiting (symptoms of ovarian torsion)
- Dizziness or fainting
Some other Less Common Symptoms
- Fatigue
- Digestive issues, and
- Breast tenderness
Recognising these ovarian cyst symptoms early helps women seek timely care and effective treatment.
What are the Risk Factors and Complications of Ovarian Cysts?
While most ovarian cysts are benign, some situations can lead to complications:
- Ovarian torsion may restrict blood supply.
- Rupture of a cyst can result in intense pain and internal bleeding.
- Cysts associated with PCOS or endometriosis can affect fertility.
- While malignancy is uncommon, it is still possible in rare cases.
Being aware of these risks and seeking timely medical care allows women to manage cysts effectively, prevent serious health issues, and safeguard fertility for the future.
How are Ovarian Cysts Diagnosed?
Accurate ovarian cyst diagnosis is essential to identify the cyst type, evaluate risks, and select the right treatment. Because symptoms can be mild or inconsistent, many women discover cysts only during routine exams or imaging.
At Indira IVF, our specialists use a combination of clinical evaluation and advanced diagnostic tools to ensure precise detection and safe management.
Pelvic Exam
During a routine pelvic exam, a gynaecologist checks the ovaries and nearby tissues for abnormal swelling, tenderness, or masses. While certain cysts, especially deep or small ones, may escape detection, the exam is still a crucial first step for evaluating pelvic discomfort or irregular cycles.
Ultrasound
For assessing cysts in the ovaries, ultrasound remains the most widely used technique. Using sound waves, it creates live visuals, helping doctors assess both the structure and size of the cyst as well as its location.
Transvaginal ultrasound, which involves a vaginal probe, improves accuracy in detecting ovarian cysts, especially smaller ones. It is a non-invasive, safe, and widely used method in reproductive medicine.
Blood Tests
Blood tests may be recommended in specific cases for extra diagnostic insight. For example, the CA-125 test measures a protein often linked to ovarian cancer.
While the majority of ovarian cysts are harmless, this test can highlight cases needing more attention. Other hormonal assessments can also help check ovarian function and uncover conditions like PCOS that contribute to cyst formation.
Laparoscopy
Persistent or complicated cysts can be treated with laparoscopy, a minimally invasive surgery where a tiny abdominal incision allows direct visualisation of the ovaries via a small camera.
Laparoscopy can be both diagnostic and therapeutic, enabling the removal of cysts or the biopsy of suspicious tissue without the need for major surgery. It is particularly valuable when imaging results are inconclusive or if there’s concern about complications such as ovarian torsion or potential malignancy.
Utilising a combination of diagnostic approaches, physicians can accurately characterise ovarian cysts, evaluate potential complications, and formulate a personalised management plan. Early and precise diagnosis mitigates symptoms and safeguards reproductive potential, which is crucial for women planning pregnancy or undergoing assisted reproductive technologies like IVF.
How are Ovarian Cysts Treated?
Most cysts are non-cancerous and self-resolving, but some require intervention to prevent complications like torsion or rupture. At Indira IVF, we customize optimal care for each patient, combining detailed diagnostics with tailored treatment to maintain ovarian health and support conception.
Watchful Waiting
Examples of functional cysts include follicular and corpus luteum cysts, which usually resolve on their own over several cycles. Infertility doctors may recommend a watchful waiting approach, using periodic pelvic exams and ultrasounds to track the cyst, while letting the body regulate ovarian function through its natural hormones.
Hormonal Treatment
Doctors may recommend hormone-based therapies, such as oral contraceptives, to women with functional cysts or PCOS to prevent cyst recurrence and formation. These treatments can also restore normal menstrual cycles, ease pelvic pain, and maintain ovarian wellness.
Surgical Removal (Laparoscopy)
Surgical intervention may be necessary for cysts that are large, recurring, symptomatic, or suspected to be complex or malignant, with laparoscopy as the favoured technique.
During laparoscopy, the surgeon uses small incisions to view the ovaries, remove cysts, and repair tissue, ensuring minimal scarring and quicker recovery. In uncommon cases, a laparotomy may be required for large or complicated cysts.
IVF Support if Fertility is Impacted
Medical interventions for cysts are most effective when supported by healthy lifestyle choices. If the patient is facing difficulty in conceiving due to ovarian cysts, the doctor may suggest undergoing IVF treatment.
Lifestyle and Supportive Measures
Eating a balanced diet, managing stress, and tracking menstrual cycles may reduce cyst recurrence and enhance reproductive health.
When Should You See a Doctor for an Ovarian Cyst?
Ovarian cysts are often harmless and may resolve on their own, but it’s important to recognise when medical attention is necessary. A quick medical assessment can protect fertility, prevent health risks, and offer peace of mind. Women experiencing persistent or severe symptoms should consult a fertility doctor.
Sudden or Severe Pelvic Pain
Sudden lower abdominal pain, sometimes sharp and severe, may indicate a ruptured cyst or ovarian torsion. Immediate medical care is essential, particularly if nausea, vomiting, or dizziness occur.
Persistent Bloating or Abdominal Swelling
Continual feelings of bloating or heaviness, or noticeable swelling in the lower abdomen, could be signs of a cyst. Persistent distension should be evaluated.
Irregular or Missed Periods
Heavier periods, irregular cycles, or extended menstruation may point to a cyst disrupting hormonal balance. Monitoring your cycle and seeing a gynaecologist can ensure timely detection.
Difficulty Conceiving
Women trying to get pregnant or those who experience delayed conception may be affected by ovarian cysts that disrupt ovulation or hormone levels. Seeking evaluation from a fertility specialist ensures early diagnosis and treatment, improving chances of conception.
Other Warning Signs
Pain during intercourse, frequent urination or urgency, and unexplained fatigue or lower back discomfort are symptoms that need attention.
Regular Check-Ups
Even if you have no symptoms, routine gynaecological evaluations are important. Early monitoring of cysts can prevent issues and preserve fertility.
Why Choose Indira IVF for Ovarian Cyst Treatment?
Choosing the best clinic for ovarian cyst management is vital, especially for women focused on fertility. Indira IVF combines skilled specialists, state-of-the-art technology, and tailored care for optimal results.
Our ovarian cyst treatment approach goes beyond simply treating cysts; it focuses on holistic fertility care, ensuring that ovarian health and future pregnancy prospects are prioritised.
Expertise and Specialised Surgeons
Our team includes highly experienced gynaecologists and specialised laparoscopic surgeons skilled in the latest minimally invasive techniques. These procedures reduce healing time, prevent excessive scarring, and safeguard ovarian tissue, supporting women who want to conceive.
Advanced Diagnostic Facilities
Accurate diagnosis is the first step in effective cyst management. Indira IVF offers state-of-the-art ultrasound imaging, comprehensive blood tests, and advanced hormonal assessments. Every cyst undergoes detailed diagnosis to assess type and potential risk, followed by a personalised treatment plan.
Holistic Fertility Care
Managing ovarian cysts safely is just one part of care; maintaining fertility is equally essential. Our approach combines cyst treatment with IVF and reproductive support to ensure women can conceive in the future.
Patient-Centric Approach
Every patient at Indira IVF receives care customised to their needs. Our team takes time to explain treatments, answer questions, and provide ongoing support. This combination of medical excellence and personalised attention creates a reassuring environment for women facing ovarian health challenges.
Effective Care
With extensive experience and a focus on fertility, Indira IVF has helped women in managing ovarian cysts while safeguarding or improving their reproductive potential. By opting for Indira IVF, women access a team of specialists, cutting-edge diagnostics, minimally invasive surgery, and comprehensive care that helps manage ovarian cysts effectively and take them closer to their parenthood goals.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Can ovarian cysts cause severe pain?
Some ovarian cysts do cause significant pelvic or abdominal pain, especially when complications like rupture or ovarian torsion occur. Functional cysts usually don’t hurt, but bigger or complex cysts can bring bloating, discomfort, or abrupt, sharp pain.
Are ovarian cysts cancerous?
Most ovarian cysts are harmless. Cancerous cysts are rare, especially but more likely in women who are postmenopausal or have a family history of ovarian cancer. Monitoring with diagnostic tests like ultrasound and CA-125 is essential for early detection.
Can ovarian cysts be prevented?
No, it is not possible to always prevent ovarian cysts. Still, maintaining regular gynaecological care, controlling hormonal imbalances, and treating underlying conditions like PCOS or endometriosis promptly can reduce the likelihood.
Can ovarian cysts affect IVF treatment success?
Yes, certain ovarian cysts may impact IVF success. If they interfere with ovulation or egg retrieval, they can pose challenges. Large cysts and endometriomas may also reduce ovarian reserve, so treatment before IVF is recommended.
Can ovarian cysts burst? What happens if they do?
Ovarian cyst rupture can occur, causing sudden, sharp pelvic pain, nausea, vomiting, or internal bleeding. Most ruptures heal naturally, but severe cases may require urgent medical attention or surgery. Signs of ovarian cyst rupture include sudden pain and lightheadedness.
What size ovarian cyst is dangerous?
Ovarian cysts over 5–10 cm or those that enlarge rapidly are often considered high-risk and may require surgery. But danger isn’t determined solely by size; symptoms and cyst type must also be considered.
Can ovarian cysts come back after being treated?
Yes, ovarian cysts have the potential to recur, particularly in women with hormonal imbalances, PCOS, or endometriosis.
How are ovarian cysts different from PCOS?
A single ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac on the ovary, but PCOS is a hormonal disorder that leads to many tiny cysts on both ovaries, along with irregular periods, weight gain, acne, and increased hair growth.
Who can get ovarian cysts?
Women of reproductive age can develop ovarian cysts. Functional cysts typically form during the menstrual cycle, while PCOS, endometriosis, or hormone problems increase risk. Postmenopausal women rarely develop benign cysts, but are checked for malignancy.
Can ovarian cysts delay pregnancy?
Yes, cysts on the ovaries can hinder ovulation, reducing natural conception chances. Large cysts or endometriosis-related cysts may postpone pregnancy, but proper management supports fertility.
Are ovarian cysts common in IVF patients?
Ovarian cysts can be common in women going through IVF, particularly functional cysts that arise during hormone therapy. Careful observation and management ensure IVF cycles proceed safely and effectively.
Do ovarian cysts affect fertility?
Some ovarian cysts may reduce fertility, especially if they disrupt ovulation, decrease ovarian reserve, or are linked to PCOS or endometriosis.
Pregnancy Calculator Tools for Confident and Stress-Free Pregnancy Planning
Get quick understanding of your fertility cycle and accordingly make a schedule to track it
Get a free consultation!