What are Ovarian Cysts?
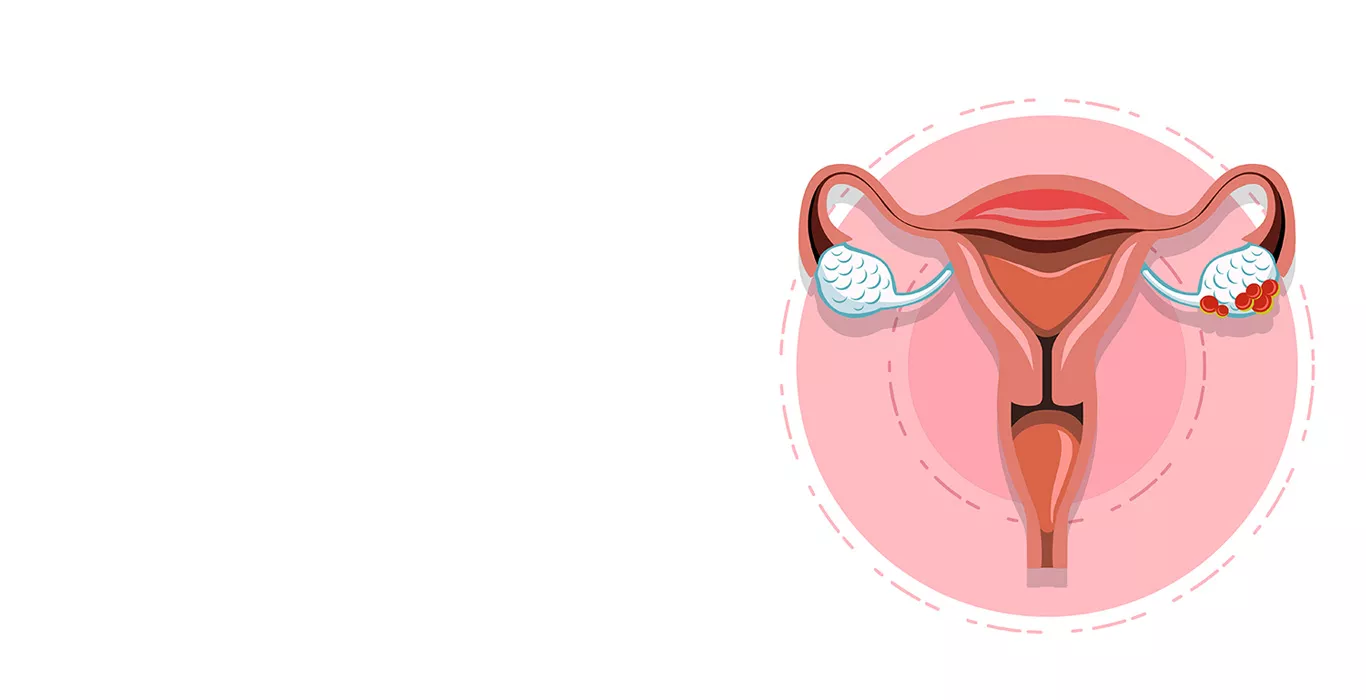
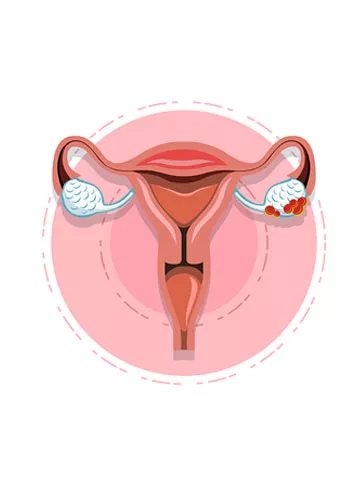
Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that develop within or on the surface of the ovaries. Ovarian cysts are a common gynaecological condition that many women experience at some point in their lives. These cysts can vary in size, from as small as a pea to larger than an orange. Most ovarian cysts are benign, meaning they are non-cancerous and often go unnoticed as they cause no symptoms. While they often present no symptoms and dissolve on their own, they can sometimes cause discomfort and, in severe cases, lead to complications.
Who can get Ovarian Cysts?
Ovarian cysts can develop in women of all ages, from puberty to menopause. They are more common during the childbearing years and can occur in those with regular menstrual cycles as well as those with irregular periods.
What are the Types of Ovarian Cysts?
There are several types of ovarian cysts, including:
1. Functional Cysts: These are the most common type and often form during the menstrual cycle. They can be further classified into follicular cysts and corpus luteum cysts.
2. Dermoid Cysts: These cysts contain tissue like hair, skin, and sometimes teeth due to being formed from embryonic cells.
3. Cystadenomas: They develop from the outer surface of the ovaries and are filled with a watery or mucous-like material.
4. Endometriomas: These cysts develop in women with endometriosis, a condition where tissue similar to the lining of the uterus grows outside the uterus.
What are the Causes of Ovarian Cysts?
The exact causes of ovarian cysts are often unknown. However, various factors can contribute to their development:
- Hormonal Imbalances: Fluctuations in hormone levels, especially during the menstrual cycle, can trigger the formation of cysts.
- Endometriosis: Women with endometriosis are more prone to developing ovarian cysts.
- Pregnancy: In some cases, cysts can form during early pregnancy to support the pregnancy until the placenta forms.
-
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): PCOS can cause the ovaries to develop multiple small cysts.
What are the Symptoms of Ovarian Cysts?
While many ovarian cysts do not cause noticeable symptoms, others can lead to:
- Pelvic pain: Dull aching or sharp pain in the lower abdomen, especially during intercourse or menstruation.
-
Bloating or swelling: The abdomen may feel full or bloated.
-
Changes in bowel habits: This can include a frequent need to urinate or difficulty with bowel movements.
-
Menstrual irregularities: Irregular or abnormal menstrual periods.
Does Ovarian Cysts Affect Fertility?
Most ovarian cysts do not negatively impact fertility. However, certain types of cysts, like endometriomas or cysts related to PCOS, may affect fertility. It's important to consult a healthcare professional if you're concerned about how ovarian cysts may impact your ability to conceive.
How are Ovarian Cysts Diagnosed?
Diagnosing ovarian cysts typically involves a combination of:
-
Pelvic Exam: A thorough pelvic examination to check for any abnormalities or tenderness.
-
Ultrasound: Imaging tests such as transvaginal ultrasound to visualize the ovaries and confirm the presence, size, and type of cyst.
-
Blood Tests: Hormonal levels may be checked to identify any hormonal imbalances that could be contributing to the cysts.
How are Ovarian Cysts Treated?
The treatment of ovarian cysts depends on various factors including the type of cyst, its size, and whether it's causing any symptoms:
1. Watchful Waiting: In many cases, especially if the cyst is small and asymptomatic, a wait-and-see approach may be taken to monitor the cyst's progress.
2. Medication: Birth control pills or hormonal contraceptives may be prescribed to prevent new cysts from forming.
3. Surgery: If the cyst is large, causing severe symptoms, or suspicious of malignancy, surgery to remove the cyst (cystectomy) or the entire ovary (oophorectomy) may be necessary.
It is essential for women to manage and seek appropriate medical care from fertility experts for ovarian cysts. Regular gynaecological check-ups and consultations with healthcare professionals are crucial in maintaining women's reproductive health.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Can ovarian cysts cause severe pain?
Yes, ovarian cysts can cause severe pain, especially if they rupture, bleed, or become twisted. The pain can be sudden and sharp, requiring immediate medical attention.
2. Are ovarian cysts cancerous?
Most ovarian cysts are benign (non-cancerous). However, some cysts can be cancerous, particularly in older women. Regular medical check-ups and appropriate diagnostic tests can help determine the nature of the cyst.
3. Can ovarian cysts be prevented?
There's no foolproof way to prevent ovarian cysts, but maintaining a healthy lifestyle, managing hormonal disorders, and seeking prompt medical attention for irregularities can reduce the risk.
4. Can ovarian cysts come back after being treated?
Yes, ovarian cysts can reoccur even after being treated, especially in cases where the underlying hormonal imbalances or conditions like PCOS persist. Regular monitoring and appropriate medical care are important to manage and prevent recurrence.
Pregnancy Calculator Tools for Confident and Stress-Free Pregnancy Planning
Get quick understanding of your fertility cycle and accordingly make a schedule to track it
Get a free consultation!